Brachial Pulse Of An Infant
Brachial Pulse Overview
During some examinations & tests, such as those with infants, the brachial pulse rate is suggested because it can be difficult to feel the radial pulse. If necessary, a Doppler may be used to locate the brachial pulse.
Technique of Measuring
Feel the bicep tendon in the region of the antecubital fossa to find the brachial pulse. To find the pulse, shift the pads of your three fingers medially (about 2 cm) from the tendon and two–3 cm above the antecubital fossa.
Key Points
It could assist to hyperextend the arm to accentuate the brachial pulse so you can experience it better. Yous may need to accommodate your fingers slightly to detect the all-time spot to reliably feel the pulse. To palpate the brachial pulse, you will normally need to push button adequately firmly.
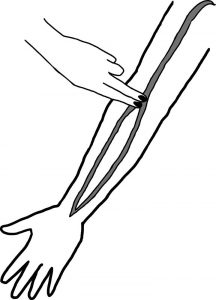
Read The Radial Artery
Measuring the Brachial Pulse in Item
Locate the Brachial Artery. Read the anatomy of the cubital fossa if you need it.
- Extend an arm and turn it so that your inner elbow is facing up. Relax your arm and slightly extend it at the elbow. It does not have to be rigid. The crease of the elbow, also known equally the cubital fossa, should be visible and easily accessible.
- But above the cubital fossa, place your fingers on your upper arm. Experience around in the area just higher up the elbow crease. You can feel a modest indent betwixt your bicep and brachialis muscles, simply above the within of your elbow. These muscles can come together around the cubital fossa's midpoint.
- If possible, use your index and centre fingers. These fingers would have the simplest time detecting the pulse. Using your index finger instead, since it has its own pulse that tin can throw off your readings.
- The brachial avenue on your inner arm should exist visible.
- To experience for a beat, keep your fingers still. The presence of a pulse means that you have located the brachial artery. The beats volition be light, close to your wrist or cervix pulse. Feel for your pulse on your neck if yous've never taken ane before. A pulse is commonly easiest to detect here. It should exist discernible on both sides of your pharynx. This gives you an idea of the kind of beat y'all should be feeling in your arm.
- If you don't feel the rhythm, adjust your fingers. If you can't feel your pulse, endeavour pushing deeper into your shoulder. Since the brachial artery is deep inside the muscle, it can need some gentle pressure to be felt. If you still can't locate the pulse, try moving your fingers around in the cubital fossa until you lot hear a thump.
- The pressure should be calorie-free and gentle. You're pressing besides difficult if you lot or the person whose pulse you're testing experiences some pain from the pressure of your fingertips.
Measuring the Brachial Pulse in Infants
- Place the baby on their dorsum, ane arm flat against their chest. The pucker of the elbow should be facing up then that you can attain information technology without moving the boy. If possible, do this while the infant isn't fussy or jumping around as well much, so you lot can become the best reading.
- Experience for a beat with two fingers just above the elbow crease. Motion your alphabetize and middle fingers gently around the baby'due south upper arm, just higher up the cubital fossa, until you experience a pulse. The beat will exist really lite, so work slowly to avoid missing it.
- To obtain a pulse reading, gently shrink your fingers. In one case you believe you've located the brachial artery, gently compress your fingers to feel the full pulse. Y'all should be compressing just enough to indent the baby's skin.
- It is difficult to find an babe's pulse. Keep distractions to a minimum and concentrate solely on the beats.
- If y'all're not certain how hard to push, ask your doctor the adjacent time yous bring your baby in for a checkup. They volition teach you lot how to test for a pulse properly.
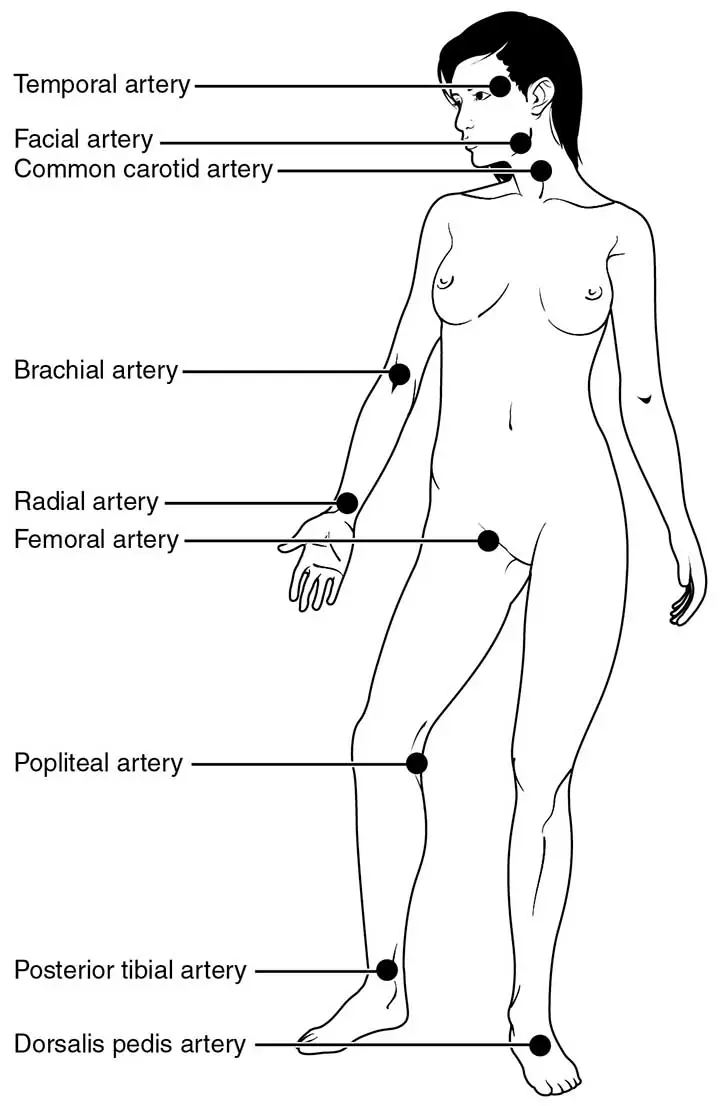
Read The Allen's Test
Counting the Pulse
Quick Count(15 seconds)
Multiply the xv-second pulse count by (4)four. The pulse counts how many times your heart beats in a infinitesimal. To go a total minute, multiply the number of thumps felt during your 15-2nd bank check by four. This gives you the full count of your 60-second pulse.
So, if you felt xvi beats while checking your pulse, multiply that by four to go a pulse rate of 64 beats per minute.
The Standard Count(60 seconds)
For the most reliable reading, check the pulse for a full 60 seconds. Taking the pulse for 15 seconds provides an authentic approximation of the overall pulse rate. Measuring the pulse for an entire 60 seconds, on the other hand, provides the most precise reading then you tin can sense the frequency and regularity of the beats. Count the number of beats from the brachial artery for sixty seconds using a clock, stopwatch, or timer.
Taking the brachial pulse for lx seconds helps you to discover missed or arrhythmic beats that might not be detected in a 15-second scan. For heart patients or those in shock, a 60-second reading is recommended.
Yous can also get a more reliable reading past repeating the 15-second count several times and calculating the average of the readings.
It's best to read pulse for lx seconds.

Clinical Points
Coronary Event Indicator
The measurement of brachial pulse pressure (PP) is a well-established adventure factor for cardiovascular disease. In young subjects, PP is primarily determined by stroke length, though the progressive amplification of pulse waves from fundamental to peripheral arteries tin can cause brachial PP to exist unrepresentative of central PP. With increasing age, brachial PP more accurately represents the gradual stiffening of the aorta and broad elastic arteries. PP is associated with vascular and cardiac hypertrophy, though the relationship with cardiac hypertrophy seems to be more closely related to systolic blood pressure (BP). Several longitudinal studies accept found a connection between PP and the occurrence of major cardiovascular events. Withal, several long-term research of subjects with mainly systolic and diastolic hypertension establish that PP is the most of import predictor of coronary events, whereas mean blood pressure is the most important predictor of cerebrovascular events. In subjects with isolated systolic hypertension, a broad PP appears to predict coronary and cerebrovascular events to a similar degree. Pathophysiologically, a wide PP may indicate diffuse atherosclerotic processes that may also include the big coronary arteries. Some evidence suggests that a large PP can too be a articulate and contained trigger for the evolution of atherosclerosis.
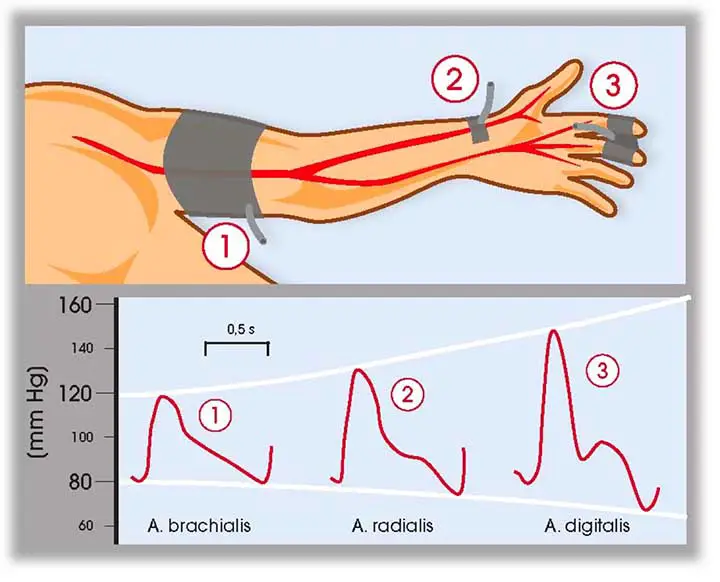
Contraindication of Measuring Claret Pressure level(Brachial Avenue)
The level of blood pressure level Continuous intra-arterial monitoring via a line inserted in the radial artery is needed in critically ill patients (or the femoral in vasoconstricted patients or where access is difficult). The brachial artery should be avoided considering it is a narrow terminate avenue whose occlusion results in hand ischemia. When in that location is systemic vasoconstriction, hateful arterial pressure level (MAP) can be normal or even high, despite the fact that cardiac output is low. In dissimilarity, if there is peripheral vasodilation, such as in sepsis, the MAP may exist poor despite a loftier cardiac output.
Circulation
The process of circulation In the collapsed or unconscious patient, the carotid pulse should be sought, merely peripheral pulses should be tested. As the shock progresses, the brachial pulse along with the radial pulse, and femoral pulses may vanish, indicating the intensity of circulatory compromise.
Venous admission for medication and/or fluid administration is critical only also difficult in ill patients. The size of the cannula required is adamant by its role. Rapid fluid administration necessitates the use of wide-bore cannulae. In the extremely hypovolaemic patient, two 16G or larger cannulae should be implanted, one in each arm. If the ii cannulae are different sizes, position the pulse oximeter on the same side as the larger i and the blood pressure gage on the aforementioned side as the smaller one. This allows for unhindered volume resuscitation and continuous oxygen saturation control. For rapid, high-volume fluid resuscitation, specially blood products, force per unit area infusors, and blood warmers should be used. For drug assistants, an 18G cannula is appropriate.
Machine-derived cuff BP measurement is unreliable at high and low blood pressures, besides as in tachycardia, especially atrial fibrillation. In hypotension, manual sphygmomanometer BP readings are more than reliable. If extreme hypotension cannot exist corrected with fluid alone, arterial line injection and vasoactive drug therapy should be considered as soon equally possible.
Brachial Pulse in Children
Sometimes it'southward hard to read the radial pulse in children. In that example, the doctors or health workers prefer the brachial pulse or popliteal pulse.
Concluding Updated on Feb 23, 2022 past Learn From Md Team
Brachial Pulse Of An Infant,
Source: https://learnfromdoctor.com/brachial-pulse-location-vital-sign-measurement/
Posted by: schacherfrob1969.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Brachial Pulse Of An Infant"
Post a Comment